Older people, professional athletes, as well as those whose work is associated with prolonged sitting or standing, often suffer from various diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Irrational daily menu, physical inactivity leads to wear and tear, destruction of bone and cartilage. As a result, lumbar osteochondrosis occurs, the symptoms and treatment of which depend on the individual characteristics of the body and the severity of the lesion.
According to the International Classification of Diseases of the 10th revision, this disease is identified by the code M42. Sometimes patients are given difficult diagnoses, and coding simplifies the work of doctors. This short alphanumeric appointment can be recorded in the medical history, on the outpatient card. So what is lumbar osteochondrosis? What are the reasons for this? What are the manifestations of the disease? This publication is about everything.
Causes of lumbar osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine often leads to injury and a slow-moving lifestyle. Among other things, one of the main roles is played by heredity, which is loaded on the body as a hormonal, chemical, psychogenic background.
If parents have lumbar osteochondrosis, the symptoms and treatment are more likely to manifest themselves and pass on to their children. Inheriting the predisposing factors, the generation is also at risk of developing this disease.
Provocateurs include the following reasons:
- Other diseases such as digestive system, liver, pelvis, nervous system;
- A leap towards slowing metabolism;
- change of acid-base balance to oxidation (acidosis);
- Decreased motor energy;
- Stress, nervous situations;
- Long awkward postures, wrong posture.
Often occurs as a result of sacral osteochondrosis, hypothermia, hormonal disorders or pathological congenital defects of the spine.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis are associated with the passage of spinal nerve fibers through the posterior region within the spinal canal. Manifestations of the disease differ depending on the localization, the severity of the defeat of some roots.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis include:
- Pain Syndrome- Most patients complain of back pain in osteochondrosis. The pain is localized directly in the area of the violation or spreads to the gluteal region, from the lesion side to the sacrum of the leg;
- sign of tension- pain increases in a certain position, but when the position of the body changes, the pain suddenly disappears. The most commonly used test is named after the explorer - Lasegue syndrome - the pain increases when the straight limb is lifted up and disappears when the foot is bent at the knee;
- Decreased or increased sensitivity- this symptom is directly related to damage to the radicular nerves, sensitivity is disturbed at a certain distance, not at the pathological site. The patient has hypoaesthesia, hyperesthesia, or paresthesia, which is characterized by unusual projection sensations, such as gas, tingling, and so on.
Often with osteochondrosis of the spine, motor activity is reduced, which is associated with varying degrees of muscle atrophy. In some cases, functions are limited, in other cases there is paralysis and paresis.
In addition, lumbar chondrosis is associated with damage to the spinal vessels, and plant changes occur with irritation and spasm. Blood circulation in the legs slows down, the lower extremities are constantly frozen, there is pallor of the skin. Other organs in the lumbar region are often affected. Thus, with damage to the bladder, urinary excretion develops or, conversely, is delayed.
Stages of the disease
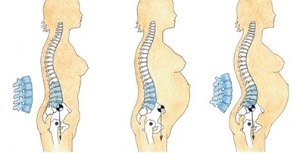
- Grade 1 lumbar osteochondrosis is the primary pathological type. It is characterized by low density of intervertebral discs. Pain syndrome occurs with a sharp turn of the body, after physical exertion or prolonged sitting.
The disease is common in drivers, office workers, athletes and people working in harsh climates. The pain is not characterized by sharp attacks, but develops as debilitating dullness or pain.
At this stage, people are not in a hurry to consult a doctor, but use traditional treatments such as ointments and compresses. The condition leads to the second stage of osteochondrosis of the spine or sacral spine;
- Grade II lumbar osteochondrosis - degenerative and dystrophic disorders of the vertebral joints. As the nuclear pulposus grows and the protrusion (protrusion) of the intervertebral disc occurs, the fibrous vertebral ring is compressed.
Neuropathologists define the second stage of osteochondrosis as lumbago. In other words, a lumbago is formed in the lumbar region when a heavy object is suddenly lifted or with other loads. This period lasts for many years, the stages of remission alternating with acute inflammatory attacks;
- Grade 3 osteochondrosis of the spine - a gradual increase in cellulite, an intervertebral hernia. The patient develops a whole range of neurological status: persistent pain, thigh, abdomen, tailbone, legs, urinary flow, limited mobility.
Used to find the legendary hernia. The diagnosis of osteochondrosis L5 S1 indicates that the bulge of the nuclear pulp occurred between the 5th lumbar and 1st cruciate vertebrae;
- When therapeutic measures are not taken in time, all stages of development smoothly move to the next stage. Stage 4 is characterized by the development of lumbar osteochondrosis complications.
As a rule, drug treatment for highly developed pathology is characterized by low effectiveness. The neurologist has to propose a radical method of action, ie hernia surgery.
Methods of diagnosing osteochondrosis
To diagnose osteochondrosis of the EPP, a neurologist first takes a medical history, as the patient's complaints are one of the crucial values for an accurate diagnosis. During the conversation, the patient is asked questions about his health and condition - what and where he is in pain, what is the duration of the pain, what makes him feel when the stiffness appears, whether the treatment is carried out, what is happening and so on.
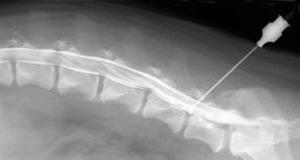
Instrumental diagnostic methods must be used:
- General view of the lumbar spine Rg-graphic image- the lumbar spine is taken as a whole or individual segments are drawn. More than others, a purposeful Rg-gram is prepared based on the doctor's complaints of disc atrophy, narrowing of the intervertebral space, the appearance of osteophytes, and smoothing of the lumbar spine;
- Myelography- Contrast fluid is injected into the canal through the spinal cord using a spinal tap. The technique is used to determine the internal structure of the channel. Ordinary people consider the procedure difficult and dangerous to diagnose, but the perforation of the spinal canal does not threaten the patient, except for contrast allergies. The puncture is performed in the absence of the spinal cord;
- Computed tomography- compression of nerve roots, pulp protrusion is determined, it is easy to see the vertebral bodies, ligaments, vessels, soft tissues at close range on the monitor;
Rather, sacral osteochondrosis is diagnosed using electromagnetic waves, for which the patient is examined on a magnetic resonance imaging scanner.
Each tissue has its own input signal, the computer processes the data and displays the image on the screen. The doctor examines the vessels, discs, bone processes, nerve fibers with a 1 mm incision. At the same time, the patient does not receive harmful ionizing effects.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
Many patients are interested in the question: what to do with osteochondrosis of the lumbar region? In lumbar osteochondrosis, there is not always an indication for surgery. The main thing is that after a thorough examination of the patient, the usual therapeutic measures are sufficient.
Conservative therapy is declining:
- Medical treatment;
- Physiotherapy procedures;
- Gymnastic exercises from sports therapy.
Manual therapy and traditional medicine are used to treat lumbar osteochondrosis.
If conservative methods for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine do not give the desired result, surgery is offered to patients only in extremely severe cases.
Medication
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis is performed by a neurologist or the narrowest specialist vertebrologist. Before treating lumbar chondrosis of the spinous processes, the doctor determines the stage and severity of pathological diseases.
Muscle relaxants are used to reduce pain, spasms, inflammation. These drugs quickly restore mobility to the patient, relieve spasms, thus relieving pain.
In addition to the group of drugs for muscle relaxation, steroid hormones are sometimes used to relieve swelling and inflammation.
Healing gymnastics
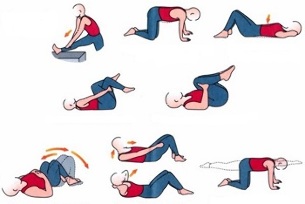
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis should be combined with sports therapy. Sports and gymnastics should be given the same attention as the use of drugs.
The therapeutic effect of osteochondrosis is exercise that relieves pain, strengthens the muscle frame, reduces compression between the discs - it slows down the further development of the disease.
Physiotherapy
Treatment for lumbosacral osteochondrosis includes the following procedures:
- electrophoresis with drugs;
- Laser and magnetic therapy;
- Treatment with magnetic currents;
- Darsonval;
- UV radiation;
- Diadine treatment;
- Shock wave method.
Manipulations involve the use of means that use natural physical force: currents, light radiation, vibration, etc. The treatment regimen, the duration of the course of physiotherapy is determined by the attending physician.
Manual therapy
When a patient asks a neurologist how to treat osteochondrosis of the spine using a hand technique, he is usually advised by a qualified specialist who not only affects the muscle tissue with his hands, but also puts the spine in place.
In lumbar chondrosis, this method normalizes blood and lymph circulation, eliminates muscle tone and deformation, and restores motor function. Chiropractor's hands reduce the clearance of spasms, reduce back pain.
How is osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine treated manually and is it possible to fully recover in this way? Manual therapy is prescribed only when the degenerative processes do not disturb the spinal tissues, ie no bone growth occurs. The need for procedures is determined by the doctor after Rg-diagnosis, CT or MRI.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of lumbar chondrosis is carried out on the basis of certain indicators, when the pathology is characterized by the following changes in the spine:
- The spinal canal narrows, the intervertebral discs are compressed and destroyed;
- Cauda equina syndrome develops - a massive nerve bundle of the spinal cone that innervates the pelvic region, the legs, is damaged;
- Loss of sensitivity progresses, there is a violation of the ability of internal organs;
- There is a risk of paralysis in the legs.
The operation is carried out according to urgent or planned indicators. The goal of surgical treatment is to reduce blood pressure and improve the condition of the spine.
Traditional medicine
Folk remedies for lumbar osteochondrosis are best done in consultation with your doctor.
Folk Pharmacy offers many remedies for the treatment of diseases:

- Medicinal plants, essential oils, flower extracts, plant roots;
- Animal products, such as snake or bee venom, badger, dog, sheep fat, boiled eggs, and more;
- Iodine, turpentine, alcohol are used for warming, irritating effects.
Similar to drugs, lumbar chondrosis is treated by folk methods only in the early stages of the disease, the symptoms are only eliminated, but the pathological changes do not disappear. Among other things, such treatments often have side effects, so you should consult a specialist before using a prescription from traditional medicine.
The dose of any folk remedy or drug should be determined by your doctor.
Complications
In the final stage, lumbar chondrosis can lead to unpleasant consequences, including disability.
Against the background of dystrophy and degenerative disorders, narrowing of the spinal canal occurs, stenosis develops. As a result of such changes, a type of chronic compression that interferes with normal blood flow occurs, vascular ischemia or cauda equina syndrome develops.
In addition, sometimes diseases such as spondylosis and spondyloarthritis develop - the intervertebral discs age, lose strength, and there is traction pain due to the damaged structure of the spinal joints. Complications are most common in the lower spine, where spinal-like bone growths occur.
In the third stage, as a complication of osteochondrosis, an intervertebral hernia develops, and diseases of the genitourinary system and other internal organs appear.Preventive measures
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine is no less important. The lower back has the greatest load, so you need to be especially careful with your back. It is worth remembering that regular gymnastic exercises are the key to the spine.
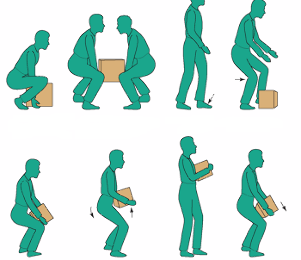
Weights should be lifted very carefully to avoid sudden concussions. Men and women can carry the burdens of the mind.
You should sit in the office and watch your posture, take the correct posture and sit in a straight chair in your chair. It is good to get up every hour, walk around the room, squat, turn the body: it relieves tension in the entire musculoskeletal system.
Trigger point massage is very good. They are active or covert. Trigger points occur as a result of excessive stress, strong stretching, repetitive work, standing, hypothermia and other factors.
Knowing the causes of spasmodic areas, it is necessary to take measures to prevent their occurrence. Recently, a trigger point massager has gained popularity, it is better to prevent the appearance of painful tricks with a special device than to treat it for a long and expensive time.























